Embarking on a journey from the bowels of the Earth to the gleaming surfaces of the electric vehicle (EV), let’s delve into the green revolution in transportation. Weaving through the labyrinth of the industry, from materials mining to supreme assembly, this article scrutinizes the sustainability of EV production. Posed with the pivotal question – Are these clean machines truly as green as they claim ‘under the hood’, or are we simply trading exhaust fumes for a lesser known environmental cost? Let’s buckle up and prepare for a deep dive into the world of sustainable EV production.
Understanding EV Production
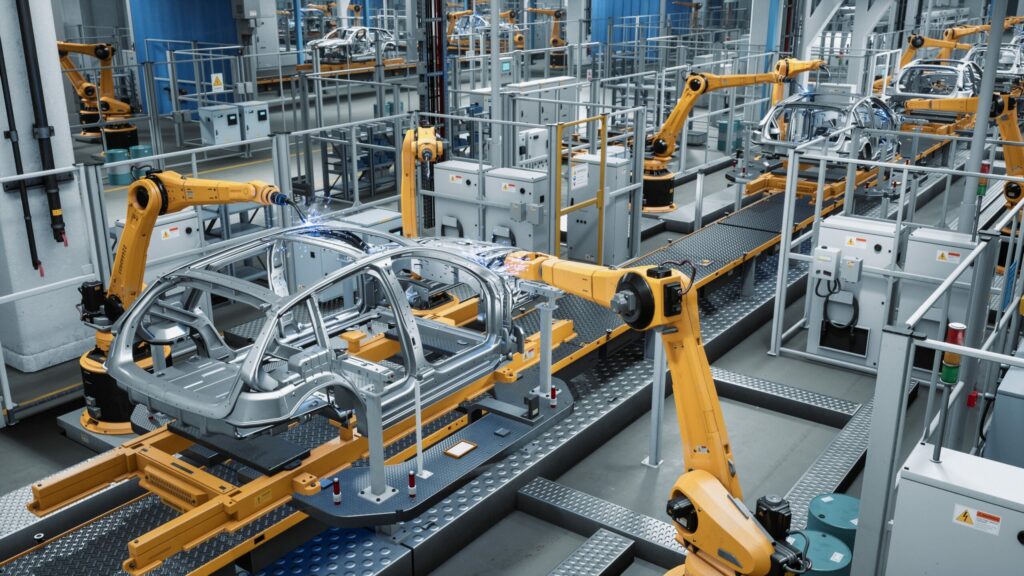

When we talk about EVs or Electric Vehicles, we’re essentially examining the environmental-friendly alternative to the traditional internal combustion engine. The allure of EVs is that they’re considered greener, touting zero tailpipe emissions. But their lifecycle, which includes their manufacturing process, is what we’re going to delve into so we can fully comprehend the ins and outs of producing these eco-trailblazers.
To kick off, what does EV production entail? Let’s break it down. The creation of an EV consists of several sequential stages: battery cell production, battery pack assembly, vehicle assembly, testing, and distribution.
Perhaps the most critical component of an EV is the lithium-ion battery, powered by lithium, nickel, cobalt and other metals. This isn’t your everyday AA battery; it’s a complex, heavily engineered piece that provides the necessary juice to power the vehicle and is the reason behind the EV’s longer range and greater acceleration. These batteries are firstly produced as individual cells. They’re then assembled into a battery pack, often integrated with a cooling system – you don’t want those bad boys overheating.
While many presume EV production to be radically different due to the absence of a conventional engine, in reality, the manufacturing process isn’t alien to what we already know. Sure, parts like the electric motor, battery pack, and power electronics would need to replace the traditional engine, but the basic automobile manufacturing tenets—stamping, welding, painting, and assembly—remain unchanged. One profound difference, however, is the incorporation of advanced automation and robotics that streamline the production process.
There’s more: aside from the manufacturing process, distribution and logistics play a vital role in this automotive symphony. Delivery from manufacturers to consumers can either be direct, somewhat Tesla’s style, or through traditional dealer networks.
Lastly, have you ever wondered what happens when an EV retires? Ideally, they’re not sent to a junkyard. Instead, many of their components, particularly their prized batteries, are recycled or repurposed for second-life applications, such as renewable energy storage.
There you have it – that’s EV production in a nutshell. Continual innovations are being made to improve efficiency and sustainability in this process, threading together different narratives of an even greener future for transportation. The next interesting subject to tackle? Sustainable mining for EV materials. But that’s a story for another day.
Sustainable Mining for EV Materials

As great as electric vehicles (EVs) are for the environment, there’s a flip side to that eco-friendly coin: the materials required for their production. These include lithium for batteries, as well as copper, nickel and other rare-earth elements. To gather these resources a thorough mining process is required. This provokes a natural question, is there a sustainable way to mine for these EV materials? Absolutely!
First, let’s consider lithium, an element so essential for EV batteries it’s brought the words ‘lithium mining’ into ecological discourse. Conventional methods can be invasive and water-intensive, but new processes in development could change that. For example, direct lithium extraction which involves drilling a hole into lithium-containing brine deposits, and using a pipe to bring the brine to the surface. The lithium is then extracted using a solvent or adsorbent material, after which the brine is returned to the ground. This minimizes surface disruption and water usage, making it a more sustainable method of lithium extraction.
Next, we’ve got copper and nickel. Automakers, aware of the environmental consequences of mining these metals, are increasingly partnering with mining companies committed to reducing their carbon footprint. This can involve the use of renewable energy in extraction processes or even the recycling of waste water.
Moreover, recycling end-of-life EV batteries could also prove a viable and sustainable source of these crucial materials. According to Reuters, just 5% of lithium and 7% of cobalt is recycled from old batteries currently, implying a huge potential for improving sustainability by simply ramping up recycling efforts. Future-tech movements, like urban mining (harvesting ‘above ground’ resources) are even considering pulling these metals from discarded tech, like smartphones and laptops.
Recalling basic high school chemistry, we go on to ‘rare-earth elements’. These are used in powerful magnets that go into EV motors. It’s actually misleading to call them ‘rare’ as they’re quite common, but the issue lies in how dispersed they are, and getting them out of the earth in useable quantities can be a dirty process. To ameliorate this concern, some carmakers are developing motors that don’t require these elements at all, designing around the problem rather than through it.
Transitioning to electric vehicles is a necessary step towards a more sustainable future. But it’s not enough to replace gas-guzzling engines with an electric powertrain. We need to address and implement environmentally responsible ways of acquiring these necessary materials. With innovation in mining methods, emphasis on recycling, and smart designs that limit the need for certain materials, we are gradually turning EV production into a completely green process.
Green Manufacturing and Assembly Processes

Viewed from a broader perspective, electric vehicles (EVs) immediately impart a vision of environmentally-friendly, ‘zero emissions’ travel. However, the sustainability aspect of EVs goes beyond emissions, commencing from the production phase itself. Here, the focus shifts towards the green manufacturing and assembly processes that elucidate a key chapter in the saga of sustainable EV production.
First things first, the manufacturing process heavily influences the carbon footprint of an EV. A significant part of this burden is attributed to energy-intensive processes and the materials being used, like aluminium and high-tech energy storage systems. Today, leading EV manufacturers are making substantial efforts to incorporate renewable energy into their production methods. From solar panels to wind farms and hydroelectric power, these energy sources are cutting down the carbon emissions involved in manufacturing, making it greener and more sustainable.
One pivotal assembly process entails battery manufacturing, arguably the heart of any EV. Using renewable energy sources to assemble these batteries significantly reduces the overall CO2 emissions of electric vehicles. Additionally, eco-friendly designs are being incorporated to ensure efficient disassembly at the end of the battery’s life, facilitating efficient recycling and reuse of precious elements.
Let’s not forget the principle of waste minimization either. Adopting a lean manufacturing approach not only lowers the operating cost but also minimizes the waste generated in the assembly process. This may include optimization of material usage, reducing packaging waste, and maintaining efficient logistics management.
Equally essential is the responsible sourcing of materials where manufacturers favor suppliers that embrace sustainable practices. This ensures a reduced environmental footprint for the entire supply chain – from raw material extraction to final assembly.
Lastly, manufacturers are investing in innovative technologies like 3D printing or additive manufacturing. Besides allowing design freedom, it mitigates waste generation, cuts down material transportation, and reduces the overall carbon footprint.
In a nutshell, the green manufacturing and assembly processes are integral to aligning the EV industry with the climate goals. Adopting such practices will move us closer to the ultimate aim of making EVs genuinely ‘green’, from mining to the wheel. So, when you slide behind the wheel of your next electric chariot, appreciate the intricate web of sustainable practices it represents – it’s certainly more than meets the eye!
Promoting Sustainability within the EV Industry
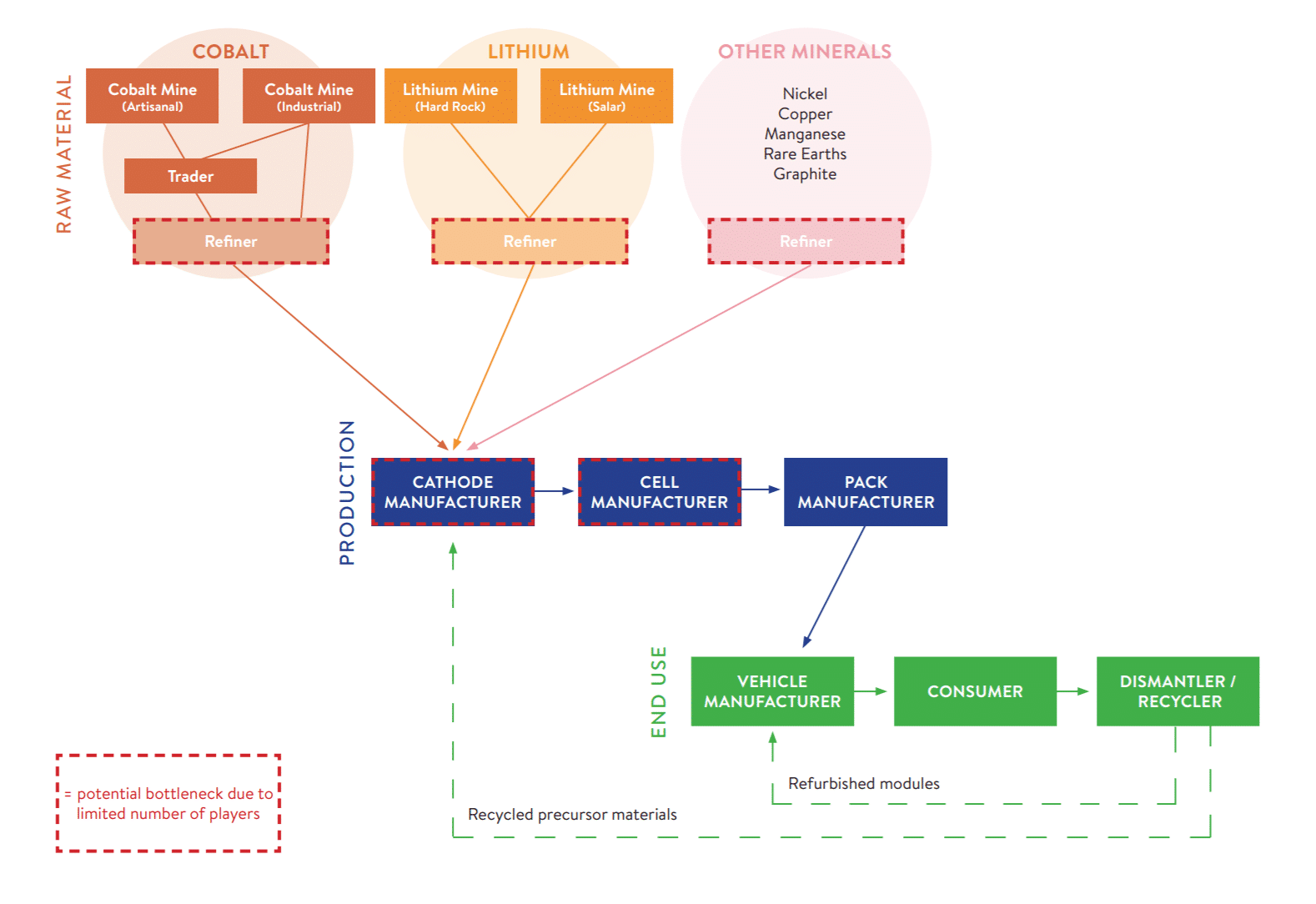
The shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) is a step towards achieving global sustainability goals. However, the industry itself needs to adopt a more sustainable approach at every stage of production, to fulfill the inherent promise of EVs.
To start, OEMs should increase their collaborations with renewable energy providers. Charging infrastructure powered by renewable sources adds credibility to EVs’ green credentials. By investing in wind, solar, and other clean energy sources, we can significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with charging EVs. After all, an EV running on coal-generated power compromises our sustainability aspirations.
Consumers also need to be actively engaged in the sustainability conversation. The EV industry will benefit greatly from educating its consumers on the higher upfront but lower lifetime costs of EVs, coupled with their environmental benefits. Consumer incentives, such as tax credits, subsidies, or preferential parking, could sway more traditional car owners towards adopting EVs.
On a systemic level, regulators and policy-makers must play a more assertive role in encouraging sustainability within the industry. Policies that influence product design and encourage the use of recyclable and less destructive materials in the production process can coax the entire industry to adhere to more sustainable practices. Stricter emission standards and regulations could further fuel the transition from internal combustion engines to electric motors.
Another significant aspect to consider in promoting sustainability within the industry is the disposal and recycling of EV batteries. EV batteries are, without a doubt, the most resource-intensive components in an electric car. It’s therefore crucial that the industry formulates efficient methods to recycle and repurpose these batteries at their end of life.
Embracing a circular economy can help too. As the adage goes, “waste not, want not.” Adopting a circular approach means designing vehicles and batteries for longevity, repair, reuse, remanufacturing, and recycling. This deceptively simple principle, when implemented at high levels in the EV industry, can make a profound difference in reducing the industry’s overall environmental impact.
In conclusion, to truly realize sustainable EV production, it’s vital to consider every stage of the process – from materials mining through to the end-of-life handling of vehicles and their components. Implementing these changes won’t be easy, but the payoff – a genuinely sustainable transportation industry – will be worth it.
FAQs
What is sustainable EV production?
Sustainable EV production? Honey, that’s when those tree-hugging engineers put on their green thinking caps to craft electric chariots without choking Mother Nature with a plastic bag. From mining those precious materials without playing whack-a-mole with our environment to assembling the gorgeous machines with, dare I say it, energy efficiency at the forefront, it’s all about keeping our planet in high spirits!
Why is sustainable material mining important for EV production?
Why you ask? Well, imagine going to your favorite bakery for a pastry, only to find out they’ve bulldozed the entire town to source their flour. That’s your answer: we can’t just wreck the planet during material mining and expect the electric magic to make up for it. That’s not the premium cable package Mother Earth signed up for.
How can assembly procedures be modified to be more sustainable?
Oh, aren’t you the brightest bulb? The assembly line isn’t just about putting all the shiny parts together. It’s also about the energy used, waste produced, and the midnight oil burned in the process. Best believe it involves more recycling than your neighborhood’s diligent trash sorter and less energy usage than a sloth on a slow day.
Conclusion
In essence, sustainable EV production is an imperative dance between technological innovation and environmental consciousness. Balancing responsible mining practices, inventive material sourcing and eco-friendly assembly process marks the dawn of a new, sustainable automotive era. Truly, it’s an exhilarating time to witness the convergence of car culture and green movement, ultimately reshaping the future of transportation with every rechargeable battery we produce.
